5. CFE tariff classification and methodology (We’ve got your back)
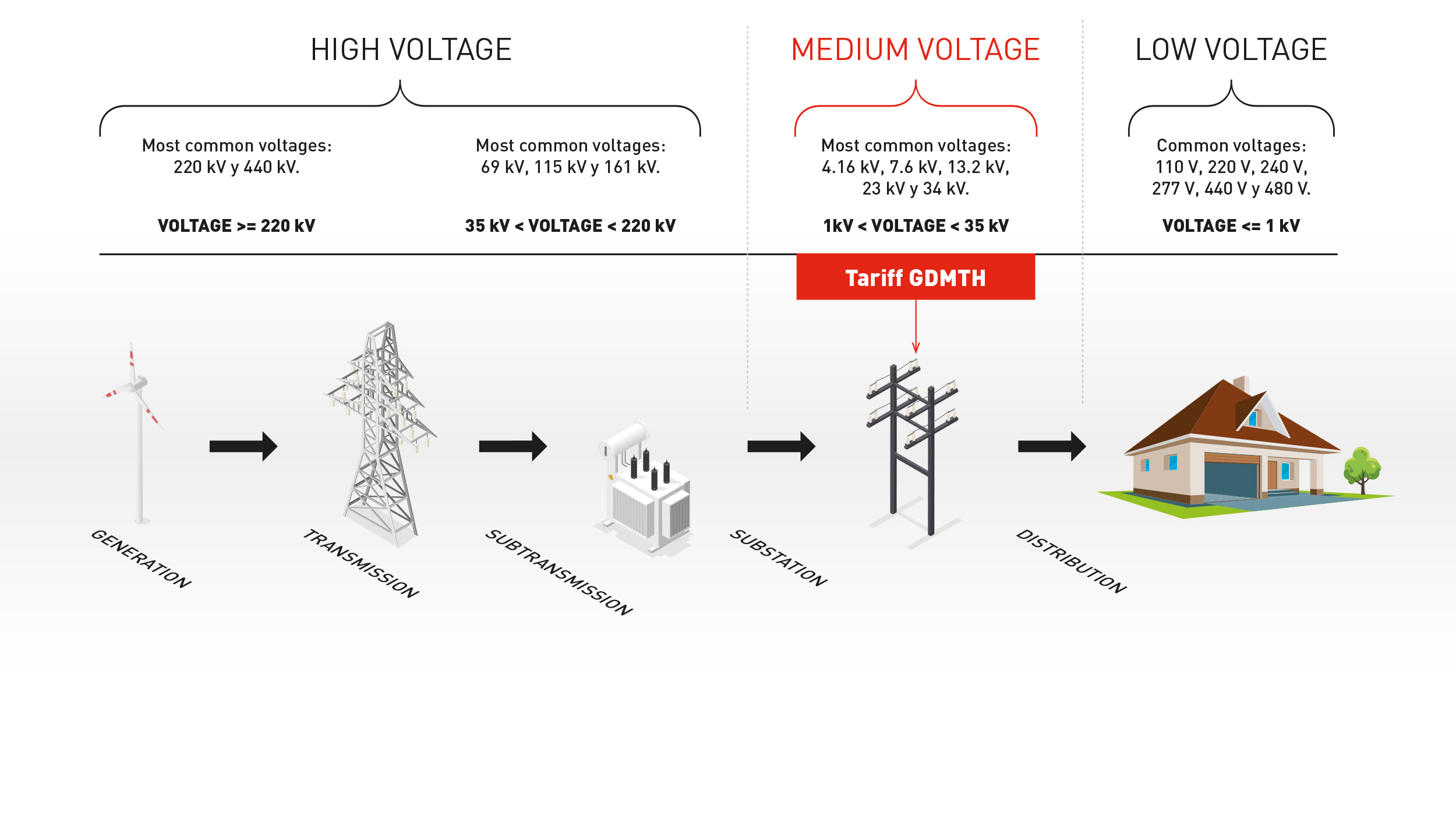
Currently we have 12 tariff categories, that divides into tariffs for households, small business and industry. In addition, they are connected into three different voltage levels – low, medium and high voltage.
https://app.cfe.mx/Aplicaciones/CCFE/Tarifas/TarifasCREIndustria/Industria.aspx
En este articulo me concentraré en las tarifas para pequeñas empresas y la industria.
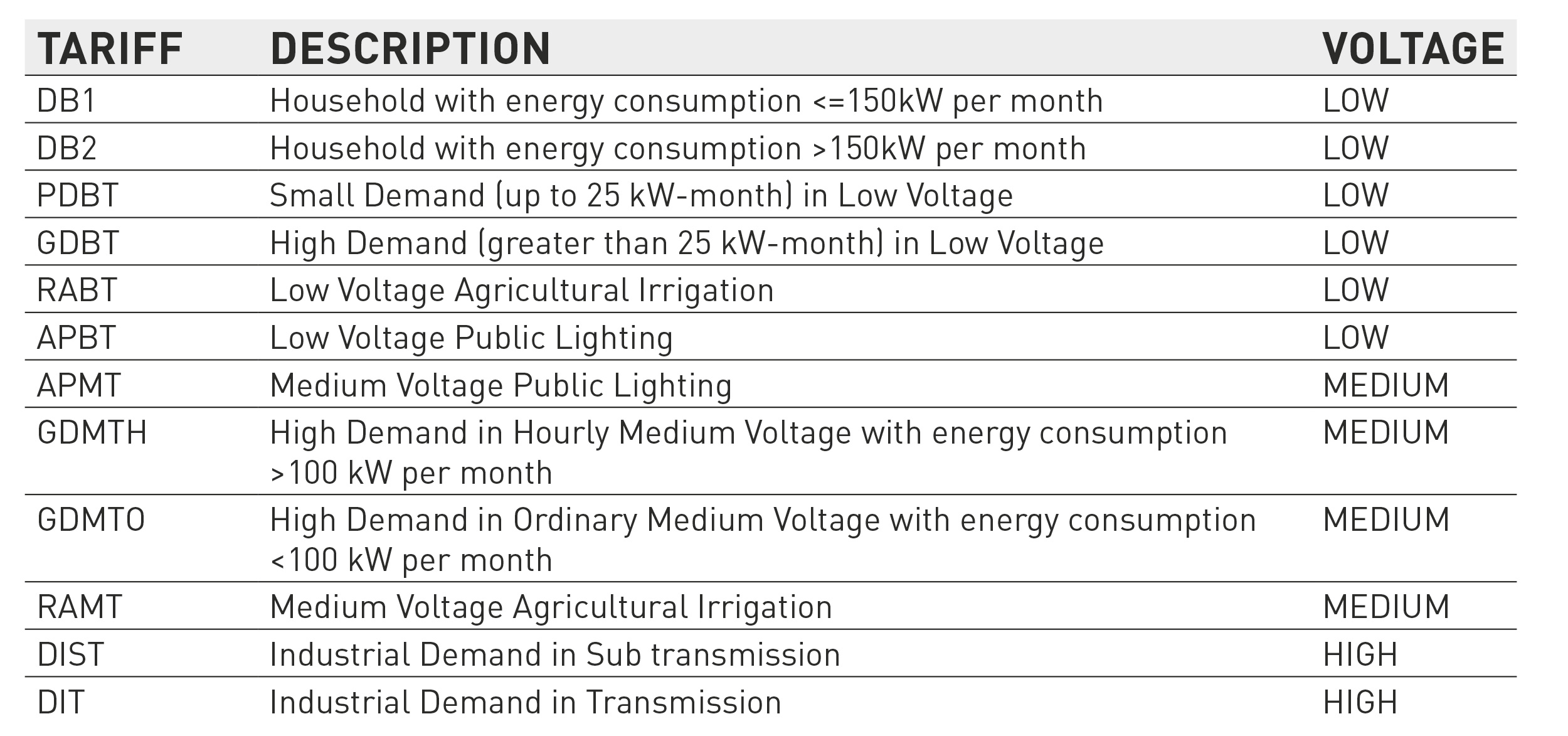
Las tarifas Bajo/Medio voltaje incluyen tarifas para propósitos específicos:
APBT y APMT – Alumbrado publico
RABT y RAMT – Agricultura
GDMTO (Gran Demanda en Media Tensión Ordinaria)
This tariff is for businesses connected to Medium Voltage and monthly energy consumption <100 kilowatts (calculated as average energy consumption of floating year). What is more this tariff doesn’t change during a day (24h).
GDMTH (Gran Demanda en Media Tensión Horaria)
Similar to GDMTO, this tariff is for Medium Voltage connections that various from 1,000 V to 36,000V and with monthly energy consumption > 100 kilowatts. This tariff has special daily scheme for calculating the price based on the consumption time. It is defined as: Basic (Base), Intermediate (Intermedio) and Peak (Punta) and it depends on location, season, day of the week and time.
DIST (Demanda Industrial es Subtransmisión)
This tariff is for industry connected to High Voltage at substation that various from 36,000 V to 220,000V. Exactly like tariff GDMTH it is divided into daily scheme. With an exception for Baja California, and Baja California Sur where it uses special Semi Peak tariff (Semipunta) for weekday during winter.
DIT (Demanda Industrial en Transmisión)
This tariff is for industry connected directly to High Voltage transmission with Voltage that various from 220,000 V to 400,000V. Like the DIST it has daily scheme for both Baja California states and one for the rest of the country SIN (Sistema Interconectado Nacional). This is the most economic tariff for the industries that depends on the quality of electricity.



